Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a common medical imaging technique with several advantages over anatomical techniques like X-ray, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Here are five key advantages of PET imaging:
1. Functional Imaging
- PET provides functional and metabolic information about tissues and organs, allowing doctors to see how well they are working. In contrast, X-ray, CT, and MRI primarily offer structural or anatomical information. This makes PET particularly useful for detecting abnormalities in cellular/tissue function, even in the absence of structural changes.
2. Early Disease Detection
- PET can detect cellular changes, such as altered metabolism, which may indicate diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s, or heart disease at an early stage. In contrast, X-ray, CT, and MRI are better at detecting anatomical changes, which typically appear later in disease progression.
3. Cancer Diagnosis and Monitoring
- PET is highly effective in cancer detection and monitoring, as it can show areas of higher glucose uptake, which is characteristic of many tumors. CT and MRI detect tumors based on size and structure, but PET provides more detailed information about tumor activity and helps in assessing the effectiveness of treatments.
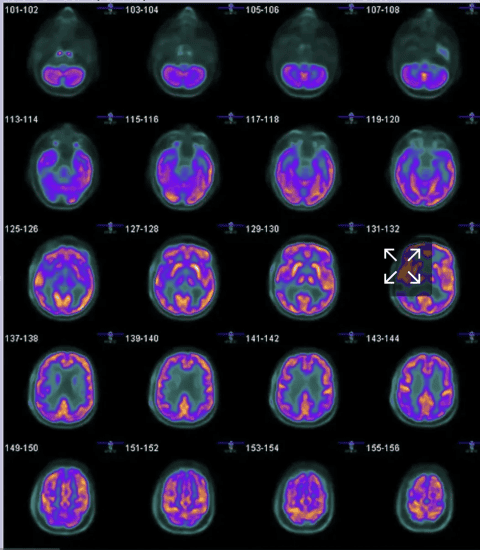
4. Precision in Mapping Brain Activity
- PET is excellent for mapping brain activity, helping to diagnose conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and epilepsy. MRI offers better structural details, but PET reveals functional changes, which is crucial in diagnosing neurological disorders.
5. Whole-body Imaging
- PET is highly effective for whole-body imaging, particularly in cancer staging, as it can reveal early metastasis by showing areas of abnormal metabolic activity throughout the body. X-ray and CT are more localized and may miss smaller or early-stage metastases.
Combined Imaging (PET/CT or PET/MRI)
- The combination of PET with CT or MRI offers the strengths of both methods — functional detail from PET and structural information from CT or MRI — enhancing diagnostic accuracy over either modality alone. The advantage of MRI is no radiation; a CT scan is essentially multiple x-rays from different angles. A disadvantage of MRI is lack of availability. There are far fewer PET/MRI machines than PET/CT scanners.
Conclusion: PET is a powerful imaging modality that can detect disease/disorder at an earlier stage and without structural changes. It is typically used in conjunction with anatomical imaging for optimal diagnostic utility.

Comments are closed.